Breast Reconstruction Surgery Turkey
Breast reconstruction rebuilds the breast after surgery or injury. In Turkey, many clinics offer this service. They use implants, expanders, or your own tissue. This is called flap surgery.
Before breast reconstruction in Turkey, meet a plastic surgeon. They’ll check if the surgery suits you. The surgeon can use implants, expanders, or your tissue. This can be done after a mastectomy or later. After surgery, follow the recovery plan. This might include rest and medicine. The goal is to boost a woman’s confidence after breast loss. Choosing a good surgeon in Turkey is key.
Whats is Breast Reconstruction Surgery
Breast reconstruction rebuilds the breast after removal due to cancer or other conditions. It helps women feel confident again. There are two main methods: using implants or the patient’s own tissue. The surgery can happen right after breast removal or later. The best time depends on the cancer type, health, and personal choice. After the surgery, patients need to rest and follow care guidelines. Choosing an expert surgeon is crucial for the best results. Breast Reconstruction Surgery Turkey
How long does it take to heal from breast reconstruction surgery?
The healing time after breast reconstruction surgery can vary depending on several factors, including the type of reconstruction performed, the individual’s overall health, and whether the reconstruction is done immediately after mastectomy or as a separate procedure. Generally, the recovery timeline can be broken down into several stages:
Immediate Post-Operative Period (First Few Days):
- Immediately after the surgery, patients typically stay in the hospital for 1-3 days.
- There is usually pain, swelling, and bruising around the surgery area.
- Drains may be placed to remove excess fluid and are usually removed within a week or two.
Early Recovery Period (First Few Weeks):
- Most women start to feel better within a couple of weeks.
- Physical activities are limited; strenuous activities and heavy lifting are usually restricted for 4-6 weeks.
- The surgeon will provide guidelines on when normal activities, like returning to work, can be resumed, typically within 3-6 weeks.
Full Recovery and Healing (Several Months):
- Full recovery can take several months.
- Swelling and scarring will gradually improve.
- Sensation in the reconstructed breast may return partially over time, but this can vary.
Follow-up Surgeries (If Required):
If additional surgeries are required, such as nipple reconstruction or symmetry procedures, this may extend the overall recovery timeline.
It’s important to follow the surgeon’s post-operative instructions closely and attend all follow-up appointments. Each person’s recovery process is unique, and it’s essential to give your body the time it needs to heal. If you experience any complications or concerns during recovery, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
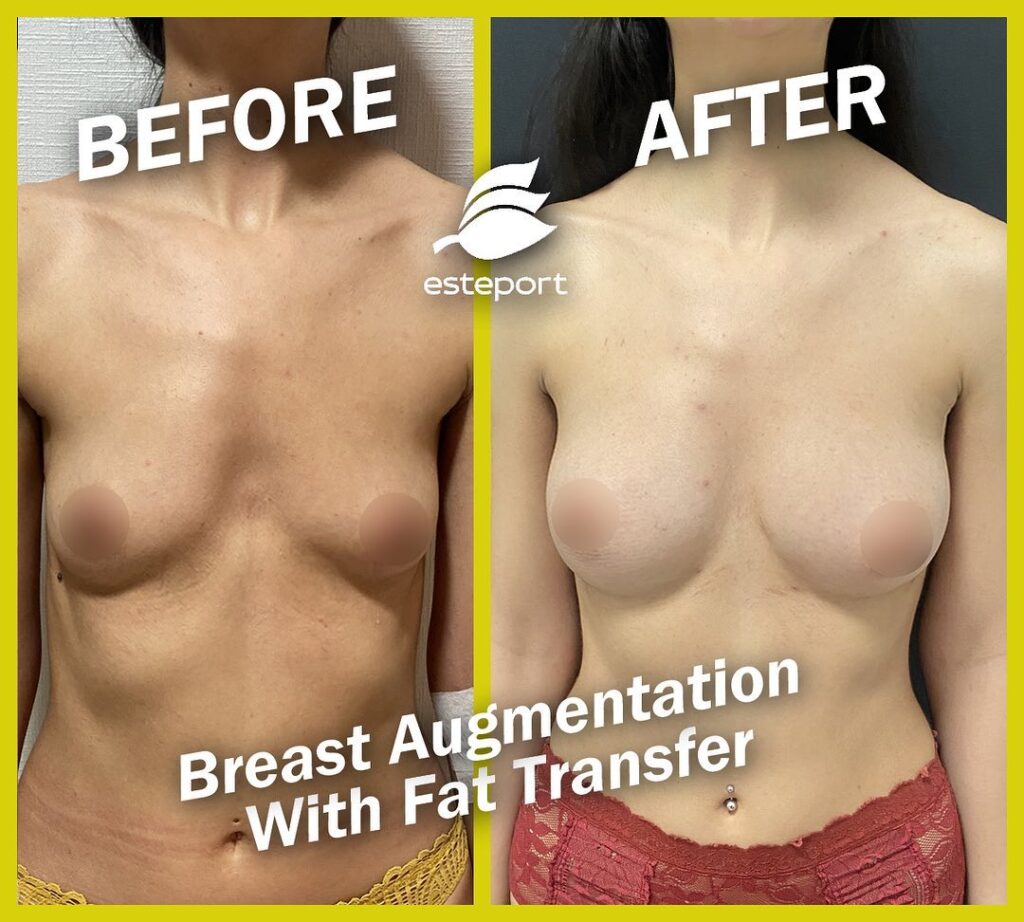
Breast reconstruction expected results
Breast reconstruction can give natural-looking results, boosting a woman’s confidence. The result depends on the surgery type, mastectomy extent, and the patient’s health. The goal is for the new breast to look like the other one. Sometimes, the other breast may need surgery for balance. Some might need extra steps, like nipple making or tattooing. Breast Reconstruction Surgery Turkey
Ideal candidates for breast reconstruction
Breast reconstruction rebuilds the breast after removal due to cancer or other issues. Not everyone can have it. Here’s who might be a good fit:
- Healthy overall: It’s a big surgery, so you need to be well.
- No issues with healing: Some conditions can make healing hard.
- Cancer-free: You should finish cancer treatment first.
- Realistic hopes: The new breast won’t feel exactly like the old one.
- Ready emotionally: It’s a big change, so you need good support and mindset.
Breast reconstruction surgical techniques
Breast Reconstruction: It’s a surgery to rebuild a breast after cancer. There are various methods:
1. Implant Reconstruction: Uses saline or silicone gel implants. Can be done immediately after mastectomy or later.
2. Autologous Reconstruction: Uses a patient’s tissue from places like the stomach or back. Gives a natural look.
3. Combination: Uses both implants and the patient’s tissue. It customizes size and look.
4. Nipple and Areola: Restores the nipple and surrounding area. Tattoos might be used.
5. Tissue Expansion: Stretches the skin for an implant. Uses a temporary saline-filled expander.
6. Fat Grafting: Fat from parts like the belly is used. It’s cleaned and then added to the breast.
7. Lymph Node Transplant: Moves lymph nodes to reduce arm swelling risks. Can be done with breast reconstruction or separately.
8. One-Stage Reconstruction: Done at the same time as mastectomy. Best for those without post-surgery radiation needs.
9. Two-Stage: Involves two surgeries. First, a pocket is created. Then, the implant or tissue is added.
10. Nipple-Sparing: Removes breast tissue but saves the nipple. Makes the result look natural.
11. DIEP Flap: Uses stomach skin and fat. Doesn’t touch muscles. This means faster recovery.
12. TRAM Flap: Takes muscle, skin, and fat from the belly. Also acts like a tummy tuck.
13. Latissimus Dorsi Flap: Uses material from the back. Often combined with an implant.
14. SIEA Flap: Uses skin and fat from the lower belly. Needs a very skilled surgeon.
15. PAP Flap: Takes skin and fat from the buttocks.
16. Gluteal Flap: Uses muscle, skin, and fat from the buttocks.
17. TUG Flap: Uses skin and fat from the inner thigh.
18. GAP Flap: Takes skin and fat from the upper buttocks.
19. Pectoralis Major Flap: Uses chest wall materials. Often paired with an implant.
20. Stack Flap: Uses multiple flaps when one isn’t enough.
RELATED: Boob Job Turkey
Preparation for breast reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Preparation:
- 1. Medical Evaluation: Patients get checked to ensure they’re fit for surgery. This includes physical checks and blood tests.
- 2. Surgical Consultation: Patients discuss options with a plastic surgeon. The surgeon reviews health history and examines the breast.
- 3. Mastectomy Planning: If getting a mastectomy, both surgeons coordinate. They might order MRIs or CT scans.
- 4. No Smoking: Patients must quit smoking. Smoking raises risks during and after surgery.
- 5. Medication Changes: Some medicines need adjustment before surgery. This means stopping some or changing doses.
- 6. Nutrition: Eating healthy helps in healing. A good diet reduces surgery risks.
- 7. Support System: Having friends or family to help during recovery is essential.
Recovery after breast reconstruction
Breast Reconstruction Recovery:
- 1. Hospital Stay: After surgery, patients might stay in the hospital a few days. Here, doctors monitor them and give pain meds.
- 2. Dressings and Drains: They help reduce swelling and infection risks. Keep them clean. Follow surgeon’s advice on care.
- 3. Activity: No heavy exercise for weeks. Start slow. Walking is good to prevent blood clots.
- 4. Pain: Surgery can hurt. Pain meds help.
- 5. Check-ups: Visit the surgeon after the operation. They check how you’re healing.
- 6. Emotions: Surgery can be emotional. Therapy or support groups can help.
- 7. Scars: Massaging and using special creams can reduce scar appearance.
Risks and potential complications of breast reconstruction
Risks of Breast Reconstruction:
- 1. Infection: Surgery can cause infection. Antibiotics might be given to help.
- 2. Bleeding: There might be too much bleeding during or after surgery.
- 3. Anesthesia Issues: Anesthesia has risks, like allergies or breathing issues.
- 4. Scarring: All surgeries leave scars. Some people might have bigger scars.
- 5. Implant Problems: Implants can rupture, leak, or move. Some need another surgery.
- 6. Nipple Loss: The nipple might not survive surgery. This changes sensation and looks.
- 7. Shape Change: The new breast might look different. This can affect how someone feels about their body.
- 8. Pain: Some might feel pain long after surgery.
Breast reconstruction surgery FAQs
Who can get breast reconstruction?
Women who had a mastectomy or have breast deformities. They should be healthy and know what to expect.
What are the types of surgeries?
There are implants, patient’s own tissue, or both. The best choice depends on the person.
How long is the surgery?
Implants take 1-2 hours. Using your own tissue takes longer.
What about recovery?
Recovery varies. Some stay in the hospital for days. Avoid heavy activity for weeks.
Can I breastfeed after?
It might affect breastfeeding. Discuss with the surgeon first.
Does it increase breast cancer risk?
No. But keep having regular breast checks.
Will insurance pay?
In the U.S., mastectomy patients get coverage. But, check your plan details.
Will the new breast have sensation?
It varies. Some feel, especially with their own tissue. Implants may feel different.
Can I have it with a mastectomy?
Yes, many do. It’s called immediate reconstruction. It can be easier for recovery and emotions.
What about after radiation?
It’s possible but more complex. You might need more surgeries.
How long do results last?
Many years. But breasts may change. Some need touch-up surgeries.
Will it affect breast cancer detection?
No. Keep doing regular checks and mammograms.
Tap here if you’re nosy about the before and after snaps!” 😜📸




Soru Sor